BORDER GATEWAY ROUTING PROTOCOL (BGP)
- Malik Zaib
- Oct 10, 2023
- 3 min read
BGP Autonomous Systems:

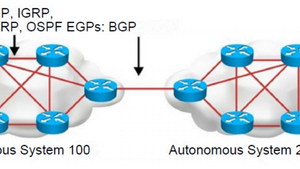
An AS is a collection of networks under a single technical administration.
· IGPs operate within an AS.
· BGP is used between autonomous systems.
· Exchange of loop-free routing information is guaranteed.
IGP –EGP:
IGP: RIP, IGRP, EIGRP, OSPF EGPs: EBGP

IGP operates within the Same Autonomous System
EBGP operates in between Multiple Autonomous System
BGP Features:
· Open Standard
· Exterior Gateway protocol
· Designed for Inter-AS Domain Routing
· Designed to scale huge inter-network like internet.
· Classless.
o Support FLSM, VLSM, CIDR, auto and manual summary (BGP-4)
· Updates are incremental and trigger
· Path vector protocol
It sends updates to manually defined neighbor as unicast
· BGP is application layer protocol uses TCP for reliability, TCP port 179
· Metric = Attributes
· Administrative distance
o 20 External updates ( EBGP)
o 200 Internal updates (IBGP)
When to use BGP
· A.S. working as transit A.S. (Ex. ISP)
A.S. connected to multiple A.S (when the AS is multi-homed) Data traffic path entering or leaving A.S needs to be manipulated.
When not to use BGP
If it is Single-home A.S
Lack of recourses like memory and less processing power in routers.
Limited understanding of BGP route filtering and path selection processes.
Types of ISP Connections
Ø Single Homed
Ø Dual-homed site
Ø Multi-homing
Ø Dual Multi-homed
Connecting to the Internet with BGP
Ø Default route from provider(s)
Ø Some routes + default route -
Ø All routes (full table) -
Single homed site
· A site with a single ISP connection is single-homed.
· This is fine for a site that does not depend heavily on Internet or WAN connectivity.
· Either use static routes, or advertise the site routes to the ISP and receive a default route from the ISP.
Dual-Homed
· A dual-homed site has two connections to the same ISP, either from one router or two routers.
· One link might be primary and the other backup, or the site might load balance over both links.
· Either static or dynamic routing would work in this case.
Multi-homing
· Multi-homing means connecting to more than one ISP at the same time.
· It is done for redundancy and backup if one ISP fails and for better performance if one ISP provides a better path to frequently used networks.
· This also gives you an ISP-independent solution.
· BGP is typically used with multi-homed connections.
Dual Multi-homed
· You can take multi-homing a step further and be dual-multi-homed, with two connections to multiple ISPs.
· This gives the most redundancy.
· BGP is used with the ISPs and can be used internally also.
Connecting to the Internet with BGP Route reception options:
Ø Default route from provider(s)
· Easy on resources, internal traffic routed to nearest BGP router
Ø Some routes + default route -
· Allows for selection of some paths with others falling back to a default route.
Ø All routes (full table) -
· Hard on resources, but guarantees the most direct path is taken
BGP Neighbors (IBGP/EBGP)
Ø BGP neighbors are routers forming TCP connection for exchanging BGP updates.
Ø Also called as BGP Peers or BGP Speakers.
Ø Two type of BGP neighbor relationship.
IBGP (Internal BGP)
EBGP (external BGP)
BGP Databases (BGP tables)
Neighbor table
A list of all configured BGP neighbors.
Has to be manually configured using neighbor command
# show ip bgp summary
# show ip bgp neighbors
BGP forwarding table/database
A list of networks known by BGP, along with their paths and attributes.
# show ip bgp
IP routing table
List of best paths to destination networks
# Sh ip route
Configuring BGP Routing Protocol
Syntax:
Router(config)# router bgp <AS no.>
Router(config-router)# network <network ID> [mask <subnet mask>
Implementation:
Router(config) #router bgp 100
Router(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.1.2 remote-as 200





Comments