Dynamic Routing Protocols
- Malik Zaib
- Oct 4, 2023
- 2 min read

What is Routing Protocol?
A routing protocol is a set of rules and conventions that routers use to figure out how to most efficiently transfer data packets from one point in a network to another. With the help of these protocols, routers may efficiently route data packets by leveraging each other's information about the network's topology and reachability.
The basic functions of routing protocols in networking:
The process of discovering and maintaining routes is facilitated by routing protocols, which enable routers to identify and build pathways to different destinations within a network. The routing tables are consistently updated and maintained in order to accommodate network modifications, such as device malfunctions or the establishment of new connections.
In situations where there are several available routes to reach a specific destination, routing protocols are responsible for determining the most optimal way by considering factors like as the number of hops, the speed of the links, and the level of congestion within the network. The objective is to identify a path that is both highly efficient and dependable.
In order to conserve bandwidth and server processing time, routing protocols use methods to eliminate routing loops. Avoiding loops is accomplished through the use of methods such as split horizon and route poisoning.
Through the use of several paths, load balancing is supported by some routing protocols. This maximizes the efficiency with which network resources are used.
The primary objective of routing protocols is to expedite convergence, wherein routers promptly establish consensus regarding the network's present condition and routing paths subsequent to any modifications.
Types of Dynamic Routing Protocols:
Basically, there are two types of Dynamic Routing Protocols
Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs)
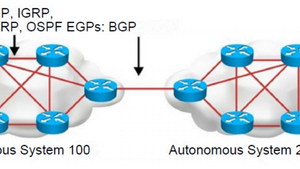
Exterior Gateway Protocols (EGPs):
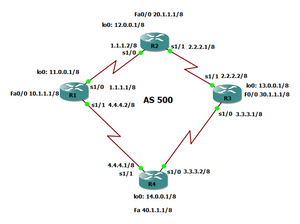
Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs):
RIP (Routing Information Protocol): A distance-vector protocol mainly used in small to medium-sized Networks.
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First): A link-state protocol designed for larger, and more complex networks.
EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol): A Cisco-proprietary protocol that combines features of distance-vector and link-state protocols.
Exterior Gateway Protocols (EGPs):
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol): Used to route traffic between different autonomous systems (ASes) on the Internet.
Routing Information Protocol for IPv6 (RIPng): A version of RIP designed for IPv6 networks.
Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS): A link-state protocol used in both interior and exterior routing, particularly in larger networks.
Specific purpose Routing protocols:
IGRP (Interior Gateway Routing Protocol): A predecessor to EIGRP, also Cisco-proprietary.
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol): Used for multicasting in IP networks.





Comments